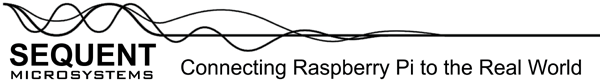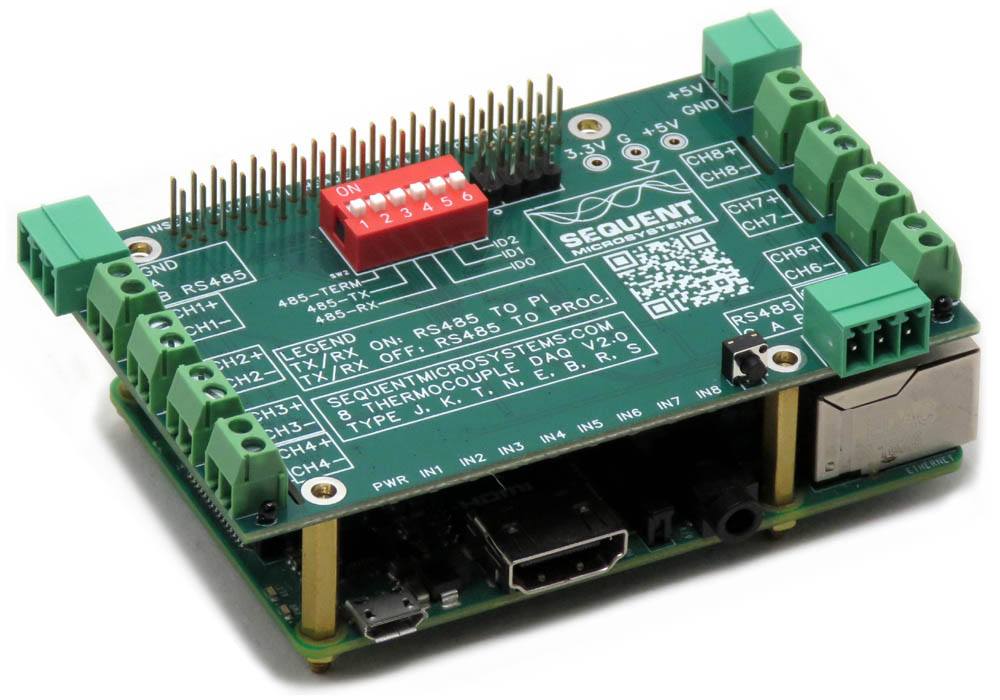
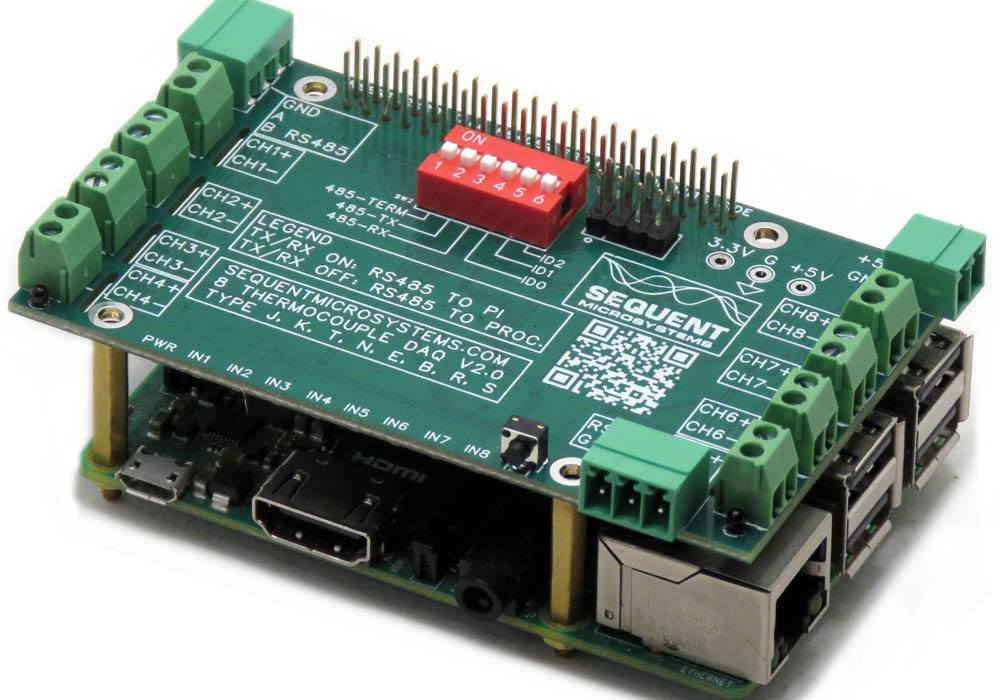
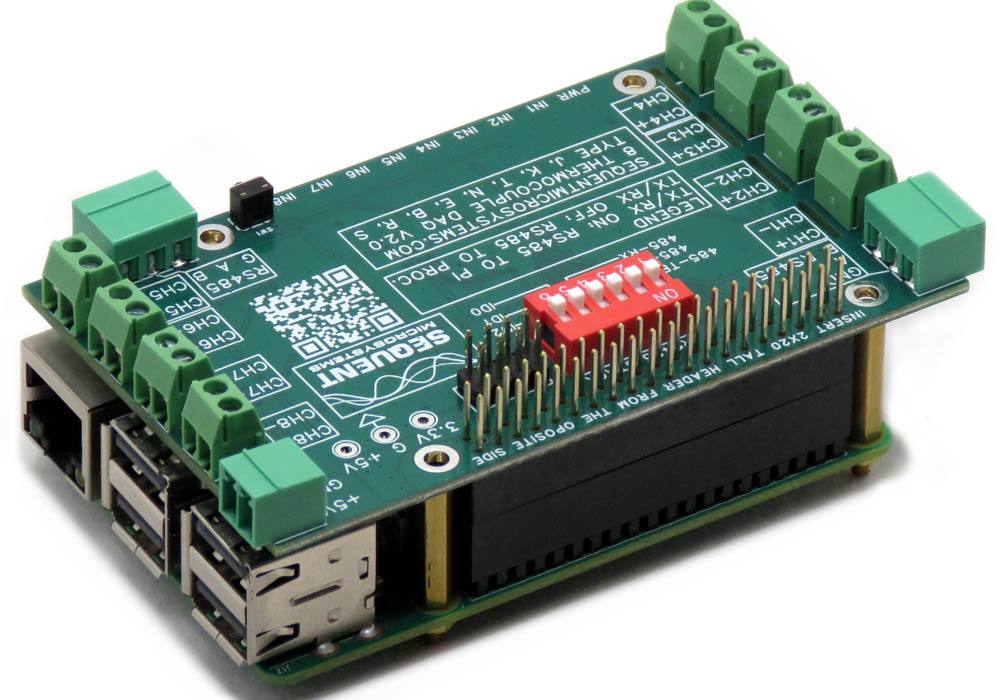







Eight Thermocouples DAQ 8-Layer Stackable HAT for Raspberry Pi
Read eight thermocouples type J, K, T, N, E, B, R and S; 0.1% accuracy through calibration; RS485, Watchdog.
FEATURES
- Eight Thermocouples DAQ 8-Layer Stackable HAT for Raspberry Pi
- Supports Thermocouples type J, K, T, N, E, B, R and S
- 24 bit delta-sigma A/D converters
- Ultra-low drift (0.005µV/ºC) low offset (50µV) amplifiers
- Factory accuracy: 1%
- Maximum accuracy (through calibration): 0.1%
- Cold junction compensation
- Maximum acquisition speed 40 cps
- RS485/MODBUS transceiver with in and out ports
- Programmable threshold LEDs on all inputs
- Pluggable Connectors 26-16 AWG wires for power and RS485
- On-board hardware watchdog
- 5V power supply provides power to Raspberry Pi
- General Purpose Pushbutton
- On-board resettable fuse
- Uses only I2C port, all GPIO pins available
- Works with any Raspberry Pi from ZERO to 5
- Command line
- Python library
- Node-RED example
- Modbus RTU
- CODESYS Driver
- OpenPLC module
- ECCN Code EAR99
- ERRATA: Polarity reversed on channels 5-8 silkscreen for VER2.0
3D FILES
8-THERMOCOUPLES DAQ HAT 3D STEP MODEL DOWNLOAD
8-THERMOCOUPLES DAQ HAT WITH RASPERRY PI STEP MODEL DOWNLOAD
DESCRIPTION
Compatible with all Raspberry Pi versions from Zero to 4, the Eight Thermocouples card offers a compact and inexpensive solution for reading and storing data from up to 64 thermocouple temperature sensors. Using 24 bit delta-sigma A/D converters with four channels each, the card achieves better than 0.1% accuracy. Field calibration with a precision 100Ω resistor can lead to 0.01% precision.
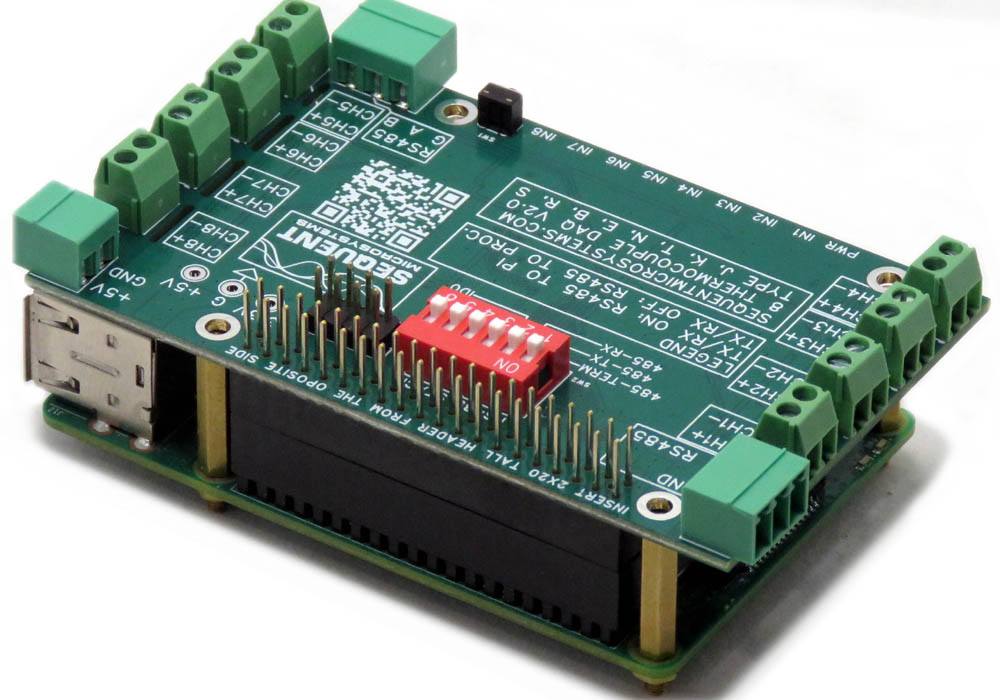
The Eight Thermocouples card is compatible with all Raspberry Pi versions from Zero to 5. It shares the I2C bus using only two of the Raspberry Pi’s GPIO pins to manage all eight cards. This feature leaves the remaining 24 GPIOs available for the user.
LED INDICATORS
DIP SWITCH CONFIGURATION

STACKING MULTIPLE CARDS
Up to eight cards can be stacked on your Raspberry Pi. Three positions of the configuration DIP Switch labeled ID0, ID1, ID2 are used to select the stack level. Cards can be stacked in any order.
RS485/MODBUS PORT
The Card has an RS485 port which can be driven from the Raspberry Pi. Set both to ON to connect the RS485 port to USART1 of the Raspberry Pi.
When DIP Switches are ON, Raspberry Pi can communicate with any device with an RS485 interface. In this configuration the card is a passive bridge which implements only the hardware levels required by the RS485 protocol.
When DIP Switches are OFF, the Raspberry Pi GPIO pins can be used for other functions. If multiple cards are stacked, only one card can have the DIP Switches ON.
RS485 TERMINATOR
The first position on the DIP switch is the RS485 line terminator. Set it to ON if the card is last on the RS485 chain.


DOWNLOADS
SOFTWARE
ACCESSORIES
YOUR KIT

- Four M2.5x18mm male-female brass standoffs
- Four M2.5x5mm brass screws
- Four M2.5 brass nuts


QUICK START
- Plug your card on top of your Raspberry Pi and power up the system
- Enable I2C communication on Raspberry Pi using raspi-config.
- Install the software from github.com:
- ~$ git clone https://github.com/SequentMicrosystems/smtc-rpi.git
- ~$ cd /home/pi/smtc-rpi
- ~/smtc-rpi$ sudo make install
-
~/smtc-rpi$ smtc
The program will respond with a list of available commands.